Achieving Robust Model Aggregation with Minimum Privacy Leakage for Federated Learning
This article investigates and implements the theory behind a recent IEEE paper released in 2024 which formalizes a novel security notion of aggregating the statistics of users' updates to provide a general framework utilizing LCC and distributed ZKPs for robust aggregation satisfying privacy concerns.
Diffusion Modeling Theory and Implementation for Learning and Generation of Data
Diffusion models have become the state-of-the-art technology for generative A.I. so we will investigate their capabilities by understanding their theoretical background and implementing their architecture.
Grammatical Learning & Generation via Hidden Markov Model Filtering, Smoothing, & Inference
For a computer to learn how and when words are organized within a sentence, it must learn to model the temporal organization of grammatical representations of words (e.g. nouns, verbs, and adjectives) and the inter-dependent probabilities by which they are realized.
Semantic Context & Analogy Prediction in Reviews via word2vec
We want to study in-detail all functionalities of the skip-gram word2vec model and implement the architecture on a corpus of restaurant reviews, with the goal of creating an embedding space for words and testing the reliability of the generated space to complete analogies.
Graph Spectral Clustering for User Preference Categorization in Social Networks
We are going to explore a fragment of the Yelp social network - a website where both restaurants and users can post food-related activity - with the goal of finding groups of users with similar restaurant preferences.
Lipschitz-Based Precoding in Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Assisted MIMO Broadcast Channels
This work addresses central mathematical issues in modern optimization efforts of wireless communications systems via Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces and offers bounds, proofs, and algorithms designed to optimize these systems and work around the induced mathematical difficulties.
EEG/MEG Signal Processing for Successive Neural Network Control
Although EEG/MEG signals exhibit notoriously low SNR, it is possible to remove much of the different sources of noise corrupting our target signals via our multi-stage processing pipeline, such that our neural network is able to optimally classify and execute further control based on these signals.
Breast Cancer Diagnosis Predictions via Logistic Regression
Where does the logistic regression model along with all of its components come from? Is it a robust model for decision making? We will investigate these questions, implement the model, and evaluate its capability to detect cancerous cells given physical tissue measurements.
California Median Housing Price Prediction via Regression & More
Often there are useful variables not directly given in a data set which can be exploited, and sometimes there are variables which offer negligible gains. After analyzing our data, we want to derive the classic linear regression model and evaluate its robustness against other classic A.I. methods.
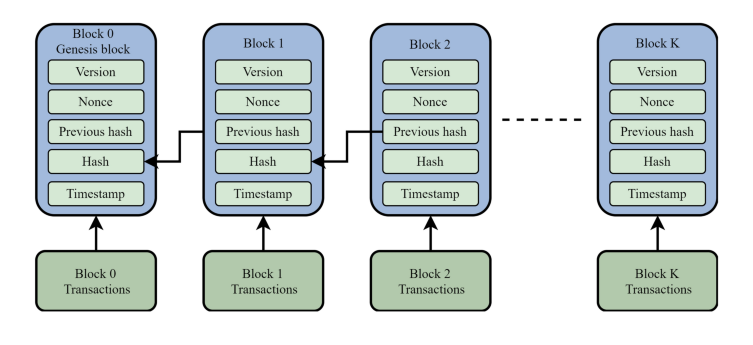
A Comprehensive Overview of Bitcoin and Blockchain Technology
The following journal investigates the technical details of blockchain technology and the Bitcoin cryptocurrency system. The journal consists of my personal notes which dive into the mathematics, protocols, and improvement proposals which have led to the Bitcoin we know today.
Adversarial Attacks, Training, & Randomized Smoothing for Increased Model Robustness
Creating adversarial examples from a given training set is a good way to increase the robustness of your A.I. model, but on its own, it does not lead to any accuracy guarantees. Randomized smoothing, however, does offer such guarantees.
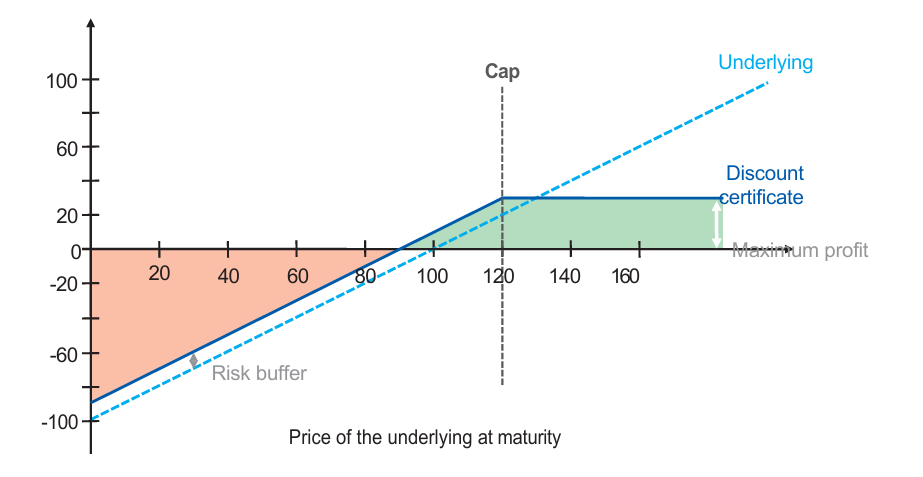
Telekom Equity-Based Bonus Certificate Pricing and Portfolio Replication via Exotic Options
Thousands of complex and highly customizable financial derivatives, known as certificates, have entered the securities markets. But how can we accurately price these instruments and construct replicating portfolios to match their payoffs or hedge against their price movements?